본 게시글은 "홍정모"님의 블로그 게시글을 참고해서 제작하였습니다.
(blog.naver.com/atelierjpro/220965203959)
Tensorflow를 C++에서 돌리고 싶을 때를 위해 미리 테스트를 했다.
Windows10 + Visual Studio 2017 (VC14.1)로 테스트를 했다.
Python 3.7 + tensorflow 2.2 버전이다.
boost는 1.73.0 버전에 python numpy 포함해서 직접 컴파일 하였다.
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 이 파일에는 'main' 함수가 포함됩니다. 거기서 프로그램 실행이 시작되고 종료됩니다.
//
#define BOOST_PYTHON_STATIC_LIB
#define BOOST_LIB_NAME "boost_numpy3"
#include <boost/config/auto_link.hpp>
#include <boost/python.hpp>
#include <boost/python/numpy.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
#include <boost/python/extract.hpp>
namespace py = boost::python;
namespace np = boost::python::numpy;
using namespace boost::python;
using namespace boost::python::numpy;
#define BOOST_ERROR(msg) ( ::boost::detail::error_impl(msg, __FILE__, __LINE__, BOOST_CURRENT_FUNCTION) )
class MyTest
{
public:
typedef boost::thread THREAD, *pTHREAD;
int a_;
MyTest(int a)
: a_(a)
{
}
int get()
{
return a_;
}
void set(int _a)
{
a_ = _a;
}
void threadjob(int tid)
{
std::cout << "Thread working! " << tid << std::endl;
}
void threadingtest()
{
const int num_threads_ = 10;
pTHREAD *thread_list_;
thread_list_ = new pTHREAD[num_threads_];
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads_; i++) thread_list_[i] = 0;
for (unsigned int thread_id = 0; thread_id < num_threads_; thread_id++)
thread_list_[thread_id] = new THREAD(&MyTest::threadjob, this, thread_id);
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads_; i++) thread_list_[i]->join();
}
void count()
{
a_++;
std::cout << "A count " << std::endl;
}
void getArray(np::ndarray& np_array)
{
std::cout << "get array c++" << std::endl;
double* ddd = (double*)np_array.get_data();
std::cout << ddd[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << ddd[1] << std::endl;
std::cout << ddd[2] << std::endl;
}
void setArray(boost::python::numpy::ndarray data) {
// Access a built-in type (an array)
boost::python::numpy::ndarray a = data;
// Need to <extract> array elements because their type is unknown
std::cout << "First array item: " << extract<int>(a[0]) << std::endl;
}
void setPointer(double* ptr)
{
std::cout << "pointer " << ptr << std::endl;
}
void set_first_element(numpy::ndarray& y, float value)
{
y[0] = value;
}
void greet(boost::python::object& obj)
{
std::cout << "Greet C++" << std::endl;
PyObject* pobj = obj.ptr();
static Py_buffer pybuf;
if (PyObject_GetBuffer(pobj, &pybuf, PyBUF_SIMPLE) != -1)
{
void *buf = pybuf.buf;
double *p = (double*)buf;
*p += 4.123;
*(p + 1) += 5.12312;
//PyBuffer_Release(&pybuf);
}
}
void plusOne(np::ndarray& np_array)
{
std::cout << "get array c++" << std::endl;
double* ddd = (double*)np_array.get_data();
ddd[0] += 1.0;
}
};
BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(my_test)
{
class_<MyTest>("MyTest", init<int>())
.def("get", &MyTest::get)
.def("threadingtest", &MyTest::threadingtest)
.def("count", &MyTest::count)
.def("setArray", &MyTest::setArray)
.def("setPointer", &MyTest::setPointer)
.def("set_first_element", &MyTest::set_first_element)
.def("greet", &MyTest::greet)
.def("getArray", &MyTest::getArray)
.def("plusOne", &MyTest::plusOne)
.add_property("value", &MyTest::get, &MyTest::set);
}
static const char * pycode = "import my_test\n"
"import numpy as np\n"
"import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf\n"
"tf.disable_v2_behavior()\n"
"mt = my_test.MyTest(123)\n"
"mt.count()\n"
"print(mt.get())\n"
"\n"
"print(mt.value)\n"
"\n"
"mt.value = 12345\n"
"\n"
"print(mt.value)\n"
"\n"
"mt.threadingtest()\n"
"\n"
"b = np.array([10.0, 20.0, 30.0], dtype = np.float)\n"
"print(b)\n"
"mt.greet(b)\n"
"print(b)\n"
"mt.greet(b)\n"
"print(b)\n"
"mt.getArray(b)\n"
"#mt.setArray(b)\n"
"#my_arr = array('f', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\n"
"#mt.set_first_element(b.array, 1123.0)\n"
"#mt.setPointer(b.data)\n"
"\n"
"input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)\n"
"input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)\n"
"output = tf.multiply(input1, input2)\n"
"\n"
"x_input = np.array([2], dtype = np.float)\n"
"y_input = np.array([3], dtype = np.float)\n"
"\n"
"with tf.Session() as sess :\n"
" print(\"Hello !\")\n"
" print(sess.run([output], feed_dict = { input1:x_input, input2 : y_input }))\n"
"\n"
"mt.plusOne(x_input)\n"
"mt.plusOne(y_input)\n"
"\n"
"print(x_input)\n"
"print(y_input)\n"
"\n"
"with tf.Session() as sess :\n"
" print(\"Hello !\")\n"
" print(sess.run([output], feed_dict = { input1:x_input, input2 : y_input }))";
void exec_test()
{
// Retrieve the main module
py::object main = py::import("__main__");
// Retrieve the main module's namespace
py::object global(main.attr("__dict__"));
py::object result = py::exec(pycode,
global, global);
py::object print = py::import("__main__").attr("__builtins__").attr("print");
print(result);
}
int main()
{
using namespace std;
//MyTest my_test(0);
// 본인의 상황에 맞게 설정한다.
// 나는 아나콘다 가상환경을 만들지 않았다.
Py_SetPythonHome(L"C:\\ProgramData\\Anaconda3");
// my_test 핸들러들을 파이썬에 등록한다.
// Py_Initialize() 함수보다 먼저 와야한다.
if (PyImport_AppendInittab("my_test", &PyInit_my_test) == -1)
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to add embedded_hello to the interpreter's "
"builtin modules");
Py_Initialize();
np::initialize();
if (py::handle_exception(exec_test))
{
if (PyErr_Occurred())
{
printf("Python Error detected");
PyErr_Print();
}
else
{
printf("A C++ exception was thrown for which "
"there was no exception translator registered.");
}
}
return 0;
}
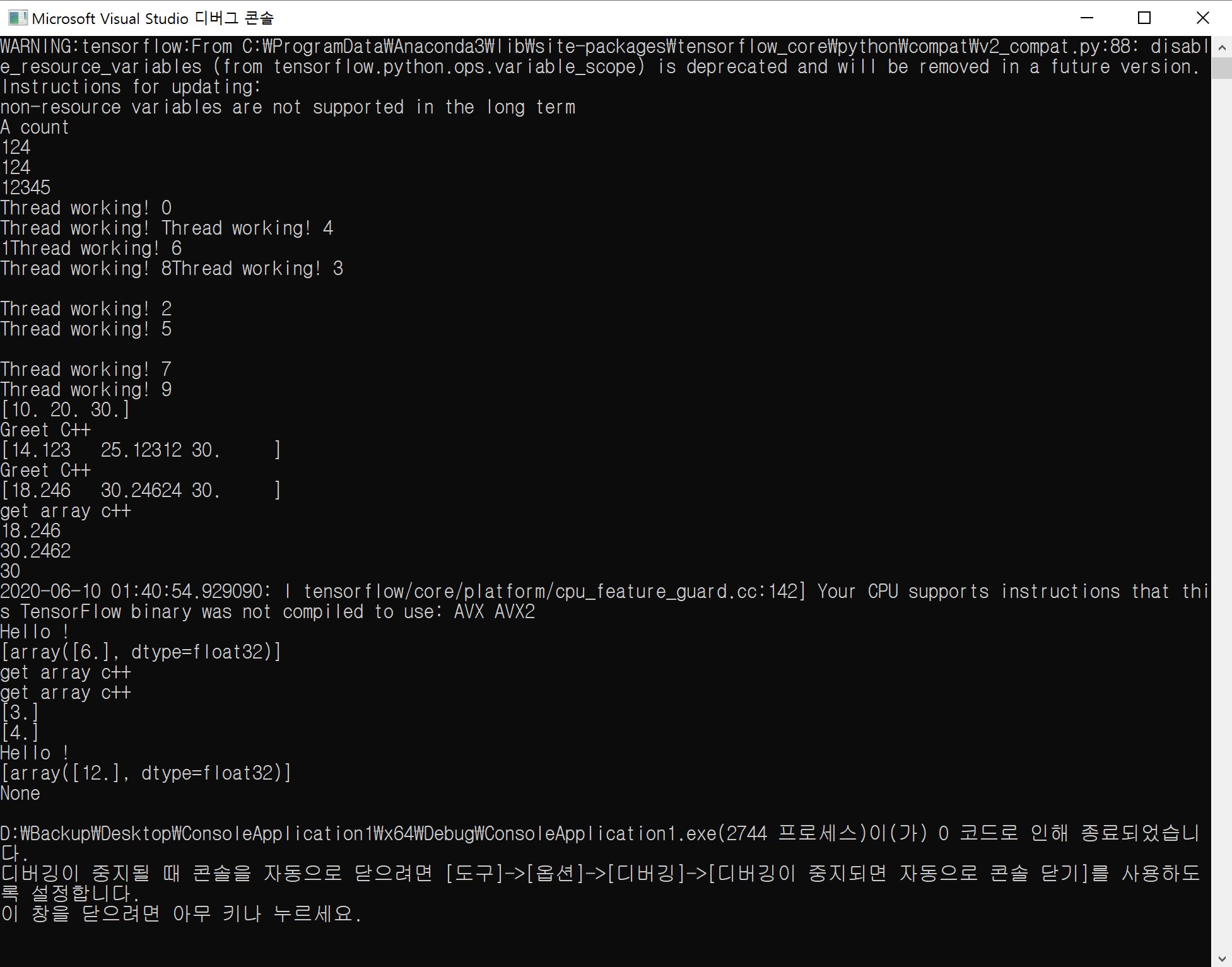
위의 소스를 실행하면 아래와 같은 결과를 보게 된다.
'Tensorflow Deep-Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [텐서플로] Tensorflow2 케라스 클래스 계층구조 (0) | 2020.06.12 |
|---|---|
| [텐서플로] C#에서 tensorflow 사용하기 (4) | 2020.06.10 |
| [BOOST] 파이썬과 C++의 동거(데이터 공유) (0) | 2020.06.10 |
| [BOOST] 빌드 방법 (0) | 2020.06.09 |
| [텐서플로] MNIST 관련 4가지 예제 한꺼번에 (tensorflow 1.x) (0) | 2020.06.06 |
